The orange circle is a locus of points with constant sum of square distances from the vertices of a pentagon ABCDE; I.e., |GA|2 + |GB|2 + …+ |GE|2 is a constant. What is the center of the circle?
Circular tension


The orange circle is a locus of points with constant sum of square distances from the vertices of a pentagon ABCDE; I.e., |GA|2 + |GB|2 + …+ |GE|2 is a constant. What is the center of the circle?

The point E moves along the outer circle whose center is G. Points A and B are fixed, whereas F and B’ vary with E. Show that F traces an ellipse as E moves along the outer circle.
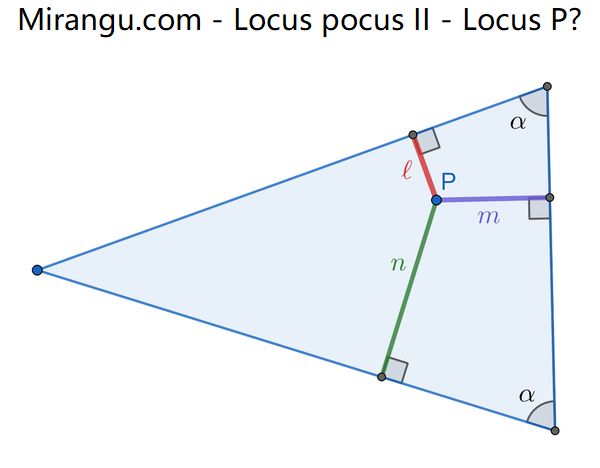
What is the locus of points P for which perpendicular lengths (red=l, green=n, purple=m) to the sides of an isosceles triangle satisfy the condition red*green = purple2?
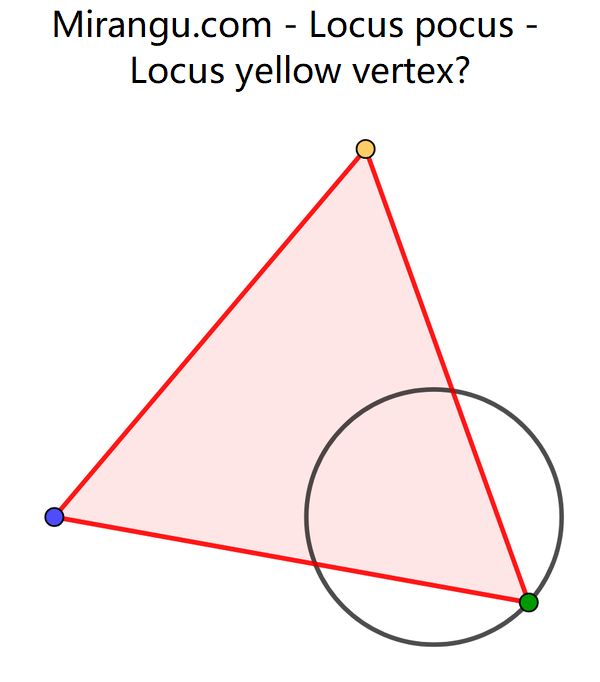
The blue vertex is fixed in the plane. The green vertex can be anywhere on a circle. The yellow vertex completes an equilateral triangle. What is the locus of the yellow vertex?
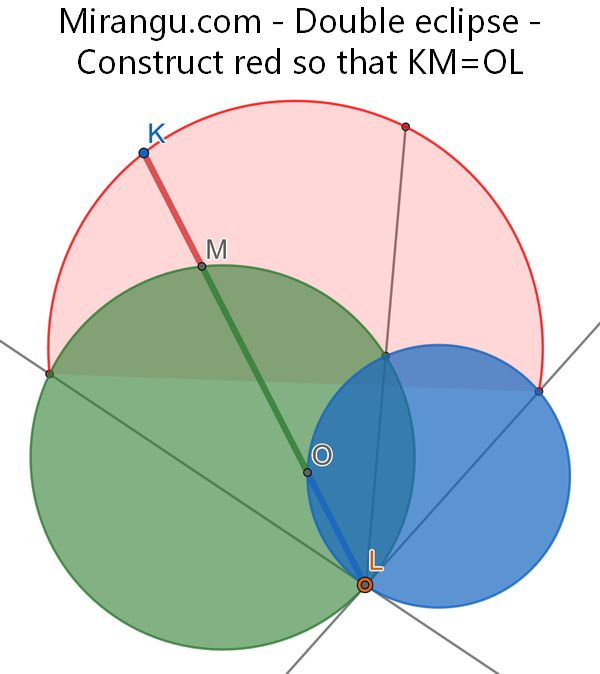
Given green and blue discs, construct a red region so that for every ray leaving L stays in the blue region exactly as long as it does in the pink region. (Namely, KM = OL.)
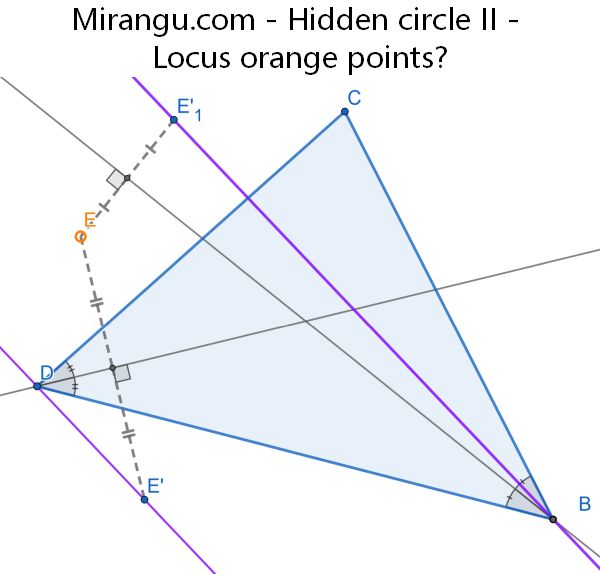
What is the locus of orange points for which the purple lines are parallel? The fixed cevians of the triangle BCD are angle bisectors.
Improve your mental health with our new book “Vitamin G, 100 wholesome geometry puzzles”.
Order now