Three circles (two with centre) and four line segments. Prove that, if the small circle is orthogonal to both wheels, then the wheels are also orthogonal to each other.
The odd bicycle
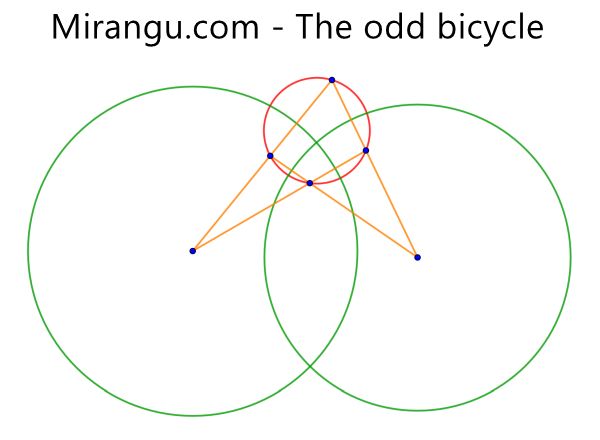

Three circles (two with centre) and four line segments. Prove that, if the small circle is orthogonal to both wheels, then the wheels are also orthogonal to each other.
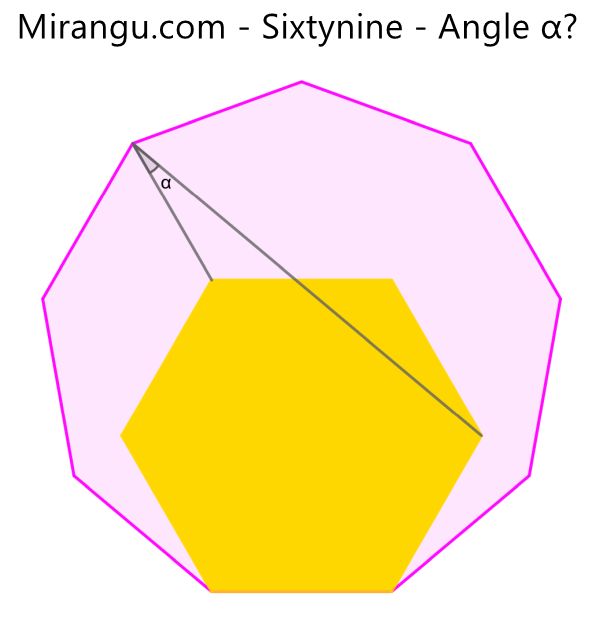
A regular hexagon shares a side with a regular nonagon. What’s the angle α?
What is the green angle α between the cross ways?

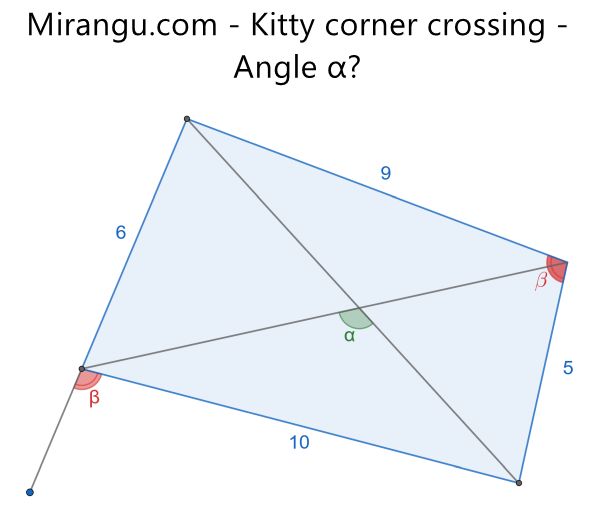
Two triangles are placed as shown. What is the angle α?
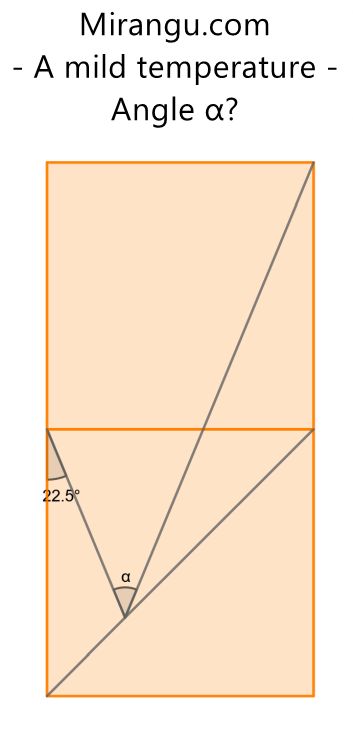
Two squares and a diagonal. What’s the angle α?
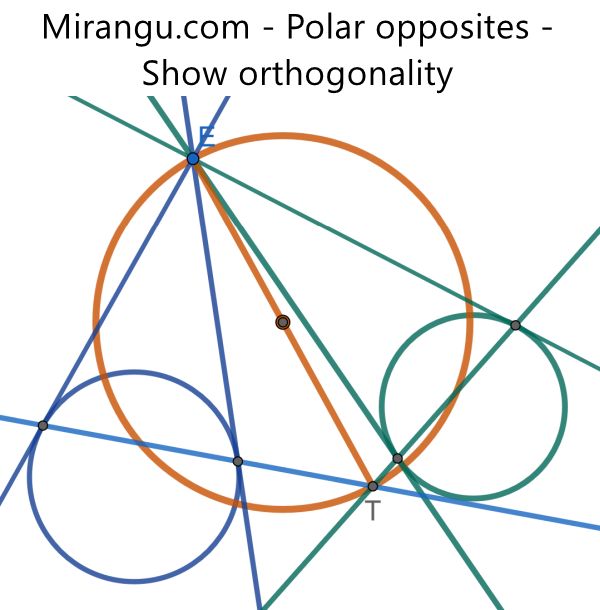
The polar lines for a point E with respect to the blue and green circles intersect at a point T. Show that the orange circle with diameter ET intersects the other circles orthogonally.
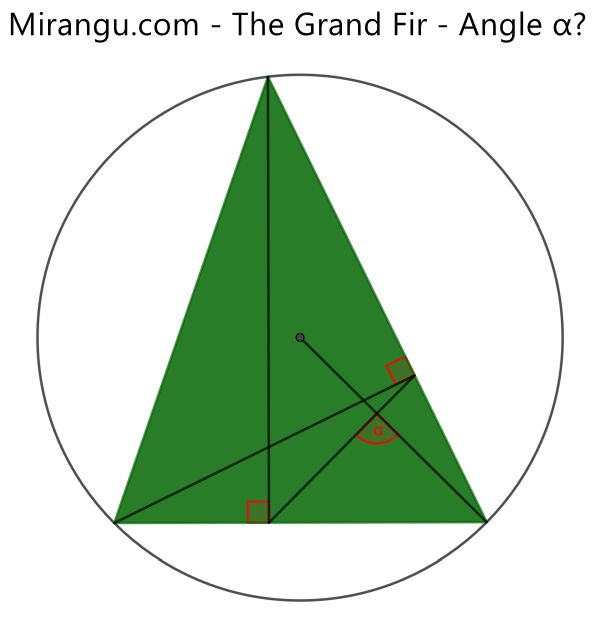
A triangle, its circumcircle, circumcentre and two altitudes. What’s the angle α?
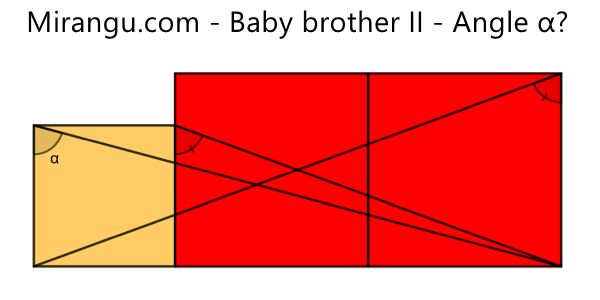
Three squares and three angles. What is the angle α?

Two squares, one of which has an extended side. Prove that the three red vertices are collinear.
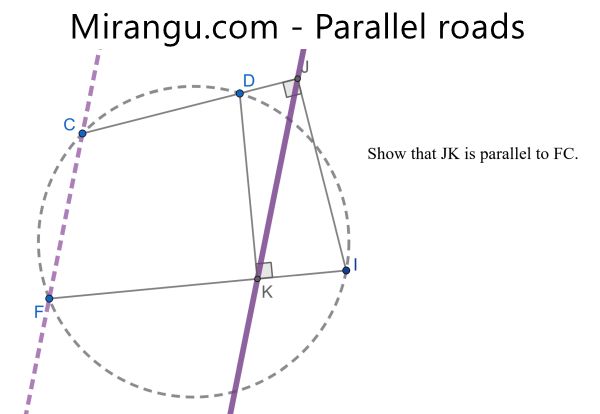
The cyclic quadrilateral FCDI, with points K such that DK perp to FI and J such than IJ perp to CD. Show that JK is parallel to FC.
Improve your mental health with our new book “Vitamin G, 100 wholesome geometry puzzles”.
Order now